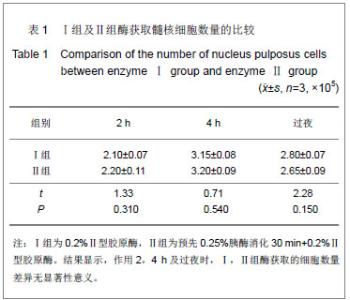
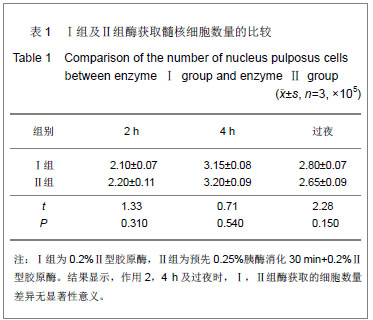
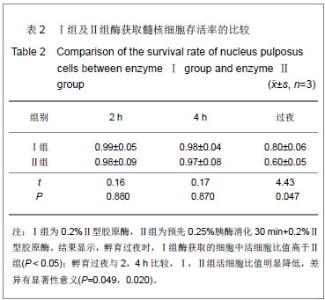
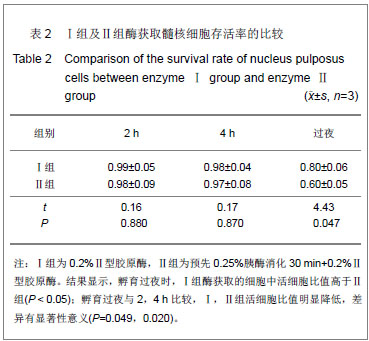
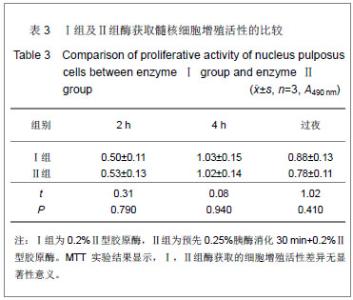
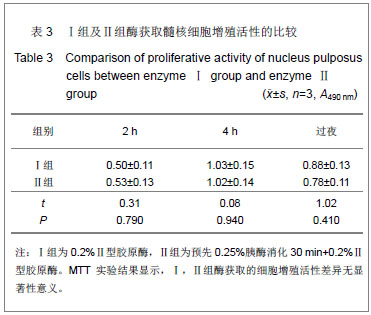
| [1]Anderson DG, Albert TJ, Fraser JK, et al. Cellular therapy for disc degeneration. Spine. 2005;30(9): 14-19. [2]Maniadakis N, Gray A. The economic burden of back pain in the UK. Pain. 2000;84(1):95-103. [3]Phillips FM, An H, Kang JD, et al. Biologic treatment for intervertebral disc degeneration: summary statement. Spine. 2003;28:99. [4]Hukins DW. Disc structure and function. In: Ghosh P (ed) Biology of intervertebral disc. CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1988: 2-37. [5]Simon SR. Kinesiology. In: Simon SR (ed) Ortho-pedic Basic Science. Am Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons, USA, 1994: 558-568.[6]Mizuno H, Roy AK, Zaporojan V, et al. Biomechanical and biochemical characterization of composite tissue-engineered intervertebral discs. Biomaterials. 2006;27(3):362-370.[7]Horner HA, Urban JP. Volvo Award Winner in Basic Science Studies: effect of nutrient supply on the viability of cells from the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc. Spine. 2001; 26(23):2543-2549.[8]Stokes IAF, Iatridis JC. Mechanical conditions that accelerate intervertebral disc degeneration: Overload versus immobilization, Spine. 2004;29(12):2724-2732. [9]Bibby SR, Urban JP. Effect of nutrient deprivation on the viability of intervertebral disc cells. Eur. Spine J. 2004;13(12): 695-701. [10]Richardson SM, Mobasheri A, Freemont AJ, et al. Intervertebral disc biology, degeneration and novel tissue engineering and regenerative medicine therapies. Histol Histopathol. 2007;22: 1033-1041.[11]Gan JC, Ducheyne P, Vresilovic EJ, et al. Intervertebral disc tissue engineering I: characterization of the nucleus pulposus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; 411(6): 305-314. [12]Deyo RA, Gray DT, Kreuter W, et al. United States trends in lumbarfusion surgery for degenerative conditions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30:1441-1447.[13]Harrop JS, Youssef JA, Maltenfort M, et al. Lumbar adjacent segment degeneration and disease after arthrodesis and total disc arthroplasty. Spine. 2008;33:1701-1707.[14]Levin DA, Hale JJ, Bendo JA. Adjacent segment degeneration following spinal fusion for degenerative disc disease. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2007;65:29-36.[15]Resnick DK, Watters WC. Lumbar disc arthroplasty: a critical review. Clinic Neurosurg. 2007;54:83-87.[16]van Ooij A, Kurtz SM, Stessels F, et al. Polyethylene wear debris and long-term clinical failure of the charite disc prosthesis: a study of 4 patients. Spine. 2007;32:223-229.[17]Pan Y, Chu T, Dong S, et al. Cells scaffold complex for Intervertebral disc Anulus Fibrosus tissue engineering: in vitro culture and product analysis. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39: 8581- 8594.[18]张荣峰,阮狄克,张超,等. 不同代次成人正常髓核细胞的形态及生长动力学比较[J]. 脊柱外科杂志, 2008, 6(3): 137-140. [19]王锋,吴小涛,王运涛, 等. 单纯Ⅱ型胶原酶消化法分离、培养人退变椎间盘髓核细胞的形态学观察[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2010, 20(4):300-304. [20]Korecki CL, MacLean JJ, Iatridis JC. Characterization of an in vitro intervertebral disc organ culture system. Eur Spine J. 2007;16:1029-1037. [21]李锋生,梁伟国,叶冬平. 体外培养人退变髓核细胞的生物学性状[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(28):9. [22]赛佳明,胡有谷,王德春. 椎间盘髓核细胞组织块法原代培养[J]. 脊柱外科杂志,2006,4(5):315-316.[23]Johnson WE, Wootton A, El Haj A,et al. Topographical guidance of intervertebral disc cell growth in vitro : towards the development of tissue repair strategies for the anulus fibrosus. Eur Spine J. 2006;15:S389-396. [24]Chen J, Baer AE, Paik PY, et al. Matrix protein gene expression in intervertebral disc cells subjected to altered osmolarity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;293: 932-938.[25]Poiraudeau S,Monteiro I,Anract P,et al. Phenotypic characteristics of rabbit intervertebral disc cells:Comparison with cartilage cellsfrom the same animals. Spine(Phila Pa 1976).1999;24(9):837-844.[26]Ishige I, Nagamura-Inoue T, Honda MJ, et al. Comparison of mesenchymal stem cells derived from arterial, venous, and Wharton's jelly explants of human umbilical cord. Int J Hematol. 2009;90(2):261-269.[27]叶冬平,梁伟国,戴丽冰, 等. 正常椎间盘髓核细胞体外不同培养代次的生物学性状分析:适应于组织工程椎间盘种子细胞的选择[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(24): 4376-4379.[28]Richardson SM, Walker RV, Parker S, et al. Intervertebral disc cell-mediated mesenchymal stem cell differentiation, Stem Cells. 2006;24(5):707-716.[29]Kandel R, Roberts S, Urban JP. Tissue engineering and the intervertebral disc: the challenges. Eur Spine. 2008;17(Suppl 4):480-491. [30]Richardson SM, Hughes N, Hunt JA, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation to NP-like cells in chitosan-glycerophosphate hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2008; 29:85-93.[31]Sobajima S, Vadala G, Shimer A, et al. Feasibility of a stem cell therapy for intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine.2008; 8:888-896.[32]Huang B,Li CQ,Zhou Y,et al. Collagen Ⅱ/hyaluronan/ chon-droitin-6-sulfate tri-copolymer scaffold for nucleus pulposus tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2010;92(2):322-331.[33]Fujita N, Miyamoto T, Imai J, et al. CD24 is expressed specifically in the nucleus pulposus ofintervertebral discs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2005;338:1890-1896.[34]Lee CR, Sakai D, Nakai T, et al. A phenotypic comparison of intervertebral disc and articular cartilage cells in the rat. Eur Spine. 2007;16:2174-2185. [35]Rajpurohit R, Risbud MV, Ducheyne P, et al.Phenotypic characteristics of the nucleus pulposus:expression of hypoxia inducing factor-1, glucose transporter-1and MMP-2. Cell Tissue Res. 2002;308:401-407.[36]Risbud MV, Guttapalli A, Stokes DG, et al. Nucleus pulposuscells express HIF-1 alpha under normoxic culture conditions: ametabolic adaptation to the intervertebral disc microenvironment.J Cell Biochem. 2006;98:152-159.[37]Roberts S,Evans H,Trivedi J,et al. Histology and pathology of the human intervertebral disc. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2006; 88(S2):10-14. |